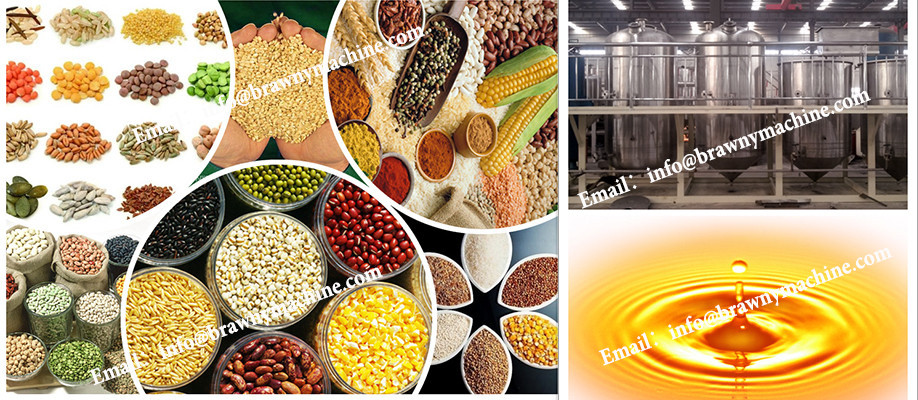
edible oil solvent extractor
Technological process introduction:
Material embryos→Extraction→Wet meal→Evaporation→Cooling→Product meal packing
↓
Mixed oil→Filter→Negative pressure evaporation → Crude oil
↓
Solvent recovery
Main economic and technical parameters:
Residual oil in meal |
≤1% (soybean) |
Solvent consumption |
≤3Kg/T(6#solvent oil) |
Crude oil moisture and volatile matter |
≤ 0.30% |
Power consumption |
≤ 15KWh/T |
Steam consumption |
≤280Kg/T (0.8MPa) |
Finished meal moisture |
≤ 10-13% (adjustable) |
Residual solvent in finished meal |
≤ 300PPM (qualified detonated experiment) |

1. Introduction
(1) Function: Leaching system is an oil extraction through soaking or spraying pre-pressed cake by a certain organic solvent. The principle of this part is the different solubility of solvent.
(2) Use range: Solvent extraction fits for pre-press extraction of high-oil-content materials and direct once time extraction of low-oil-content materials.
(3) Main parts: The extraction series includes rotary extractor, toaster, 1st evaporator, 2nd evaporator, stripping tower, condenser, etc.
2. Main Process
(1) The material (for pretreatment) is sent to rotary extraction by the scraper conveyor. The material will extracted by the solvent or mix oil. After this step, we will get meal and mix oil.
(2) Meal is sent to toaster. Through the toaster, the solvent in the meal will separate from the meal. The solvent goes to condenser and is recycled to rotary extraction.
(3) After the mix oil from the rotary extraction enters into 1st evaporator and 2nd evaporator, most of the solvent in the mix oil is separated.
(4) The mix oil from 2nd evaporator goes to stripping tower and almost all the solvent is separated. From the stripping tower, we can get crude oil and solvent. The solvent is sent to condenser and is recycled to rotary extraction.
